B.E. Curriculum 2023
Overview & ELOs
The course plans are created in accordance with the program’s expected outcomes. During their first year, students typically take general education courses required by the university, as well as some foundational concepts in economics and quantitative tools used for upper-level study. Then, students begin taking more major subject courses in their second year. Most registered courses are intermediate-level subjects that serve as a solid foundation for upper-year economics subfield courses.
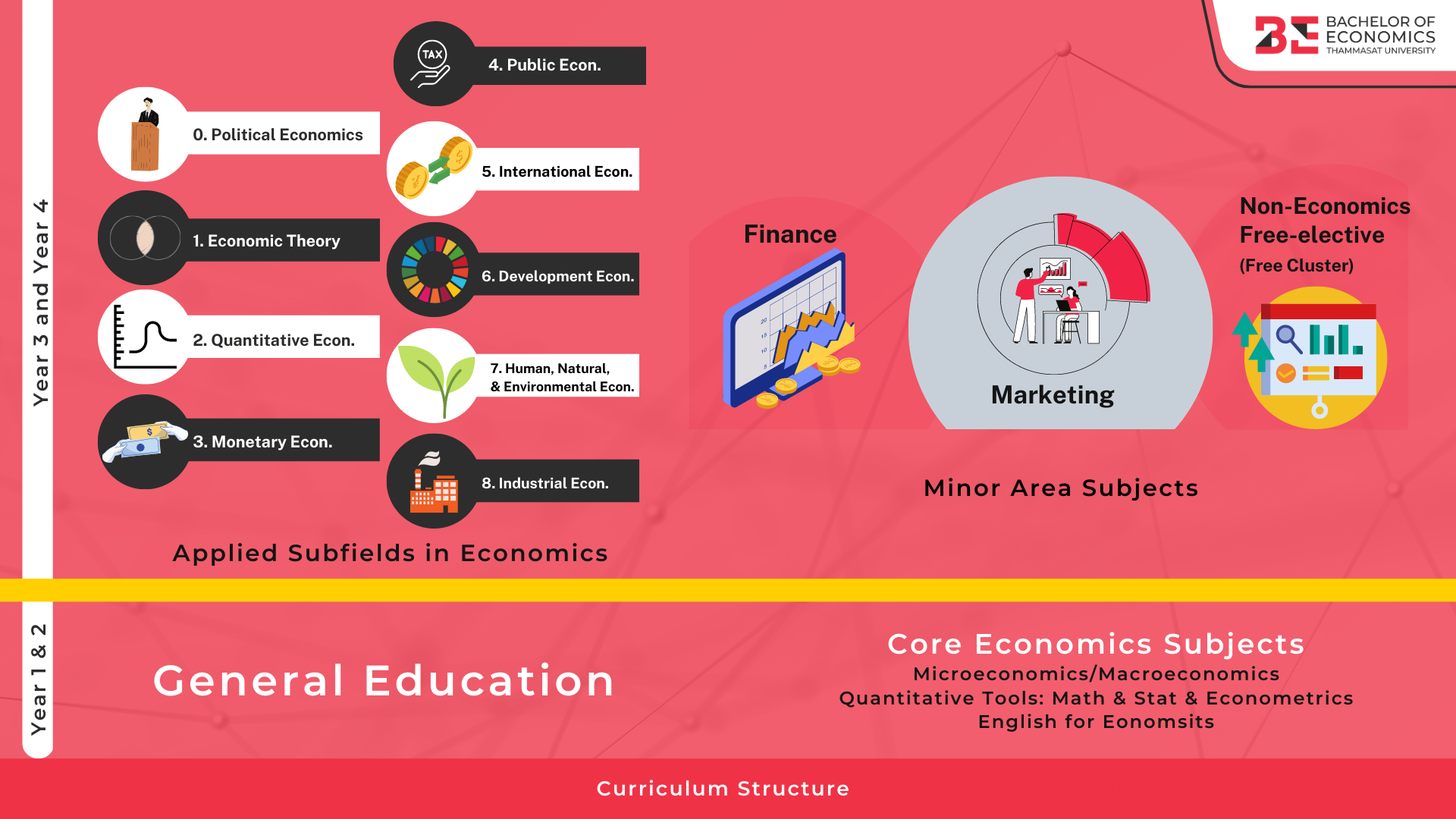
Having entered their third year, students can delve deeper into the real-world applications of economic principles by choosing from a wide range of topics or issues covered in several economics subfield courses.
We offer nine subfields in economics at the B.E. international program. Each subfield area in economics is not only linked to various career options that students may pursue after graduation, but also provide conceptual framework, tools and knowledge needed for a completion of a required capstone project in their final year. The capstone project is a one-semester (a seminar subfield course) or one-year (the honor thesis) project in which students must conduct independent research on a topic to gain a thorough understanding of it. The project can be an individual or collaborative work at the discretion of the class supervisor, but it must reflect a decent quality of research project. Under each type of capstone class (seminar subfield course or honor thesis), the project investigator will assist students in developing high-level thinking skills for use in research, guiding students until the project is completed.
At the B.E. international program, students have not only been provided with rigorous economic knowledge, but the 2023 curriculum also intends to prepare students for a variety of career options. In addition to their economics major courses and selected subfield economics courses, students may enroll in a variety of non-economics courses. Enrollment credit for these courses may be counted toward a minor field of study degree. The B.E. International Program offers three minor fields of study: finance, marketing, and free-cluster. All minor courses are taught by Thammasat business school professors and industry practitioners with certified charter.
Ranking | Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs) | Learning Process | Assessment Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
Knowledge
| |||
K1 |
Acquiring knowledge and understanding of economic theories, fundamental economic tools, theory development, and applied economics
|
1. Lecture on theoretical knowledge 2. Problem-based learning by emphasizing problem analysis/problem-solving 3. Independent study by assigned research papers and academic projects 4. Training sessions on quantitative analysis and using technology for processing, analysis, interpretation, and effective presentation 5. Demonstrating knowledge integration in related study fields 6. Brainstorming to encourage active learning and applied knowledge |
1. From assigned homework/projects/reports/ research papers 2. From quizzes and exams 3. From case study analysis/displaying knowledge and conceptual understanding |
K2
| Ability to apply theoretical knowledge to analyze and provide practical suggestions for economic and social issues | ||
K3 | Ability to appropriately integrate economic knowledge with other study fields
| ||
K4 | Ability to attain lifelong learning and thoroughly understand world economic and societal changes and impacts | ||
Ranking | Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs) | Learning Process | Assessment Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
Skills | |||
S1 |
Acquiring intellectual skill and ability to think systematically to identify research topics, perform research, process data, and evaluate findings
|
1. Problem-based learning by emphasizing analysis of problems/problem-solving sources 2. Brainstorming to encourage class discussion and applied knowledge 3. Preparing research papers/projects 4. Training sessions on essential technology for education, work, and lifelong learning 5. Written and oral presentations using technology 6. Soft skills and extracurricular learning activities |
1. Quizzes and examinations 2. Observation of participation in analytical thinking and proposing problem-solving guidelines 3. From the ability to use mathematical and statistical techniques to process data, analyze, interpret, and propose suggestions as shown in a report/assignment 4. From extracurricular activity participation 5. From self- and peer- evaluated participation and personal development |
S2 | Acquire analytical and communication skills and ability to interpret data from different sources, analyze, and integrate knowledge to propose appropriate problem-solving guidelines for economic and social issues
| ||
S3 | Acquire quantitative and technological skills for research studies | ||
Ranking | Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs) | Learning Process | Assessment Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
Ethics | |||
E1 |
Acknowledge moral values and exhibit ethical traits, including decency, selflessness, and integrity
|
1. Learn from case studies covering ethics-related topics 2. Incorporating moral value instruction in lectures and class discussions 3. Assigning independent research projects 4. Assigning group research projects 5. Participating in analysis and providing ethical insights in case studies 6. Experiencing real-life situations 7. Developing social responsibility activities |
1. From punctuality, class participation, and meeting deadlines 2. Observation 3. Peer- and self-reflections 4. Assessment forms |
E2 | Showing self-discipline, social responsibility, and good citizenship
| ||
E3 | Respect rights, opinions, values, and dignity of others. Obey organizational and societal rules and regulations
| ||
E4 | Developing professional ethics
| ||
Ranking | Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs) | Learning Process | Assessment Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
Character | |||
C1 | Ability to effectively complete assigned tasks and responsibilities |
1. Individual/group assignments 2. Lecture/debate/ brainstorming/class discussion/knowledge sharing 3. Encourage asking questions in class to promote student engagement 4. Activities to encourage problem-based learning by emphasizing analysis of problem /problem-solving sources 5. Involvement in problem-solving processes by projects/research papers 6. Oral presentation 7. Extracurricular learning experiences |
1. Assignment quality 2. From problem-solving processes 3. From observations of behavior/research presentations/projects/ assignments 4. From ability to convey leadership and teamwork in different situations 5. From teamwork skills and problem/case study analysis 6. Examine thought processes, connected thinking, and reasoning |
C2 | Ability to initiate problem analysis independently and/or in teamwork | ||
C3 | Acquire leadership and collaborative skills and respect different viewpoints | ||
C4 | Show active learning characteristics and aspire to personal development
| ||
C5 | Acquire interpersonal skills and ability to collaborate and adapt to changing circumstances
| ||
Subfield in Economics | Example of Possible Career Choices |
|---|---|
Political Economics | Public Policymakers NGO Economists |
Economics Theory Quantitative Economics | Bank of Thailand Academic Economists Data-Analytic Economists |
Monetary and Financial Economics | Central Bank Economists Financial Sector Economists |
International Economics | International business and finance |
Public Economics | Public Policymakers Fiscal Authority Staff |
Development Economics | Development & Planning Economists Public Policymakers International Labor Organization Corporate Sector Economists Social Enterprise Firms, World Bank Economists |
Environmental & Natural Resources Economics and Human Resource Economics | Human Resource Department International Labor Organization Corporate Sector Economists |
Industrial Economics | Business Consulting Firms Industry Regulators |
Curriculum Structure
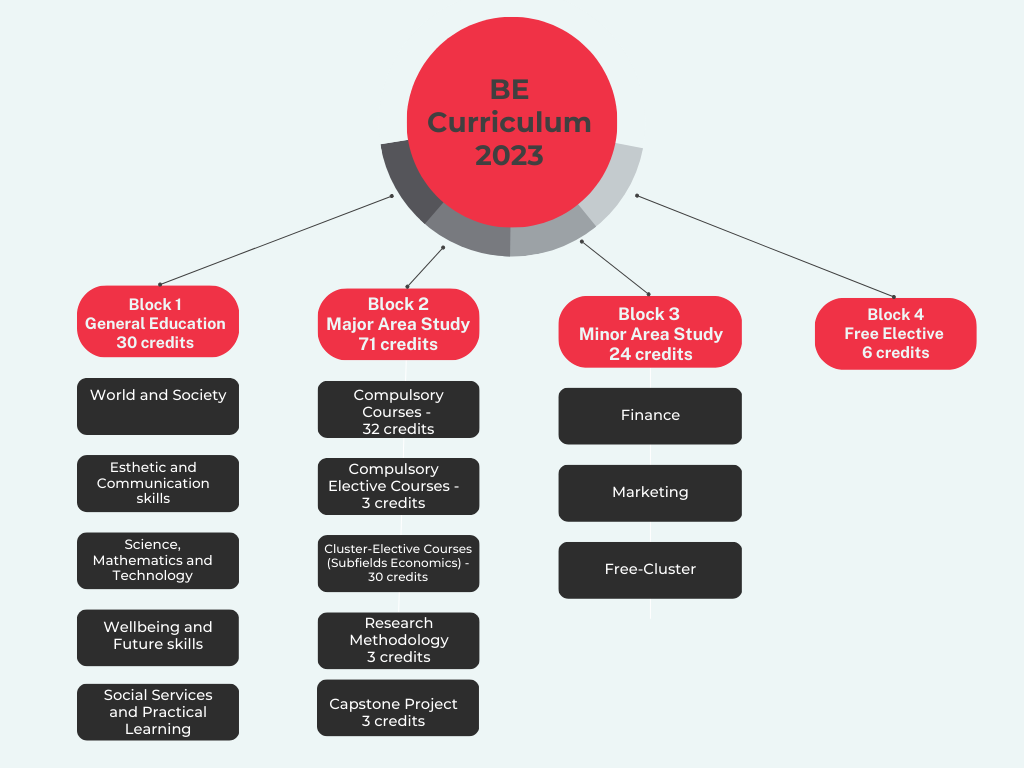
The Bachelor of Economics, International Program requires students to register a minimum of 131 credits in accordance with the course structure and distributed requirements as follows:
Block 1) General Education Courses | 30 | credits
|
Block 2) Major Area Courses | 71 | credits
|
2.1) Compulsory Courses
| 35 | credits
|
2.2) Compulsory Elective Courses
| 3 | credits
|
2.3) Cluster-Elective EE-title Courses
| 30 | credits
|
2.3.1) Cluster-Elective EE-title Courses 1 (Cluster-Specific Compulsory Courses: EE-title courses with 400-level or higher code)
| 21 | credits
|
2.3.2) Cluster-Elective EE-title Courses 2 (Cluster-Specific Elective Courses: EE-title courses with 300-level or higher code)
| 9 | credits
|
2.4) Research Methodology
|
3
| credits
|
2.5) Capstone Project or Seminar
|
3
| credits
|
Block 3) Minor Area or Non-Economics Elective Courses
|
24
| credits
|
Block 4) Free Elective Courses
|
6
| credits
|
General Education (Gen-Ed) Courses are divided into five areas of subjects. Students are required to complete a minimum of 30 credits in Gen-Ed courses in accordance with the following course structure.
1. Students must study at least one subject in each of the five areas of Gen-Ed courses. For B.E. curriculum 2023, we require a total of 15 credits which consists of 9 credits of compulsory courses, 6 credits of compulsory elective courses in the following list.
World and Society: 1 compulsory course (3 credits)
TU101 Thailand, ASEAN, and the World
Esthetic and Communication skills: 1 compulsory course (3 credits)
TU106 Creativity and Communication
Science, Mathematics and Technology: Students must complete at least 1 course (3 credits) in following list
TU103 Life and Sustainability, or
TU107 Digital Skill and Problem Solving
Wellbeing and Future skills: Students must complete at least 1 course (3 credits) in following list
EL295 Academic English and Study Skills 1, or
TU108 Self Development and Management
Social Services and Practical Learning: 1 compulsory course (3 credits)
TU100 Civic Engagement
2. Students must collect another 15 credits from the Gen-Ed courses specified and offered by the B.E. program:
a.TU122
b.TU116
c.Other Gen-Ed courses offered by B.E. program
World and Society: 1 compulsory course (3 credits)
| ||
TU101 Thailand, ASEAN, and the World | 3 (3-0-6)[2] | |
Science, Mathematics and Technology: Students must complete at least 1 course (3 credits) in following list
| ||
TU103 Life and Sustainability | or | 3 (3-0-6)
|
TU107 Digital Skill and Problem Solving | 3 (3-0-6) | |
Wellbeing and Future skills: Students must complete at least 1 course (3 credits) in following list | ||
EL295 Academic English and Study Skills | or | 3 (3-0-6) |
TU108 Self Development and Management | 3 (3-0-6)
| |
Social Services and Practical Learning: 1 compulsory course (3 credits) | ||
TU100 Civic Engagement | 3 (3-0-6)
|
3 (3 – 0 – 6) is referred to a course with 3 credits, 3-hour lecture, 0-hour laboratory session, and 6-hour self-study.
Block 2.1 Compulsory courses 32 credits
2.1.1) MA216 (or MA211) and ST216 (or ST211)
2.1.2) EL241 and EL341
2.1.3) EE211; EE212; EE311; EE312; EE320 (or EE421) and EE325 (or EE425)
Block 2.2 Compulsory elective courses 3 credits: students are required to complete 3 credits from one of the following courses specified by the faculty.
2.2.1) EE404 History of Economic Thought, or
2.2.2) EE406 Contemporary Economic Issues, or
2.2.3) EE460 Thai Economy
Block 2.3 Cluster-Elective EE-title courses 30 credits consisting of cluster-specific compulsory courses and cluster-specific elective courses as follows
2.3.1) 21 credits of EE-title (elective) course with 400-level or higher code.
2.3.2) 9 credits of EE-title (elective) course with 300-level or higher code.
Block 2.4 Research methodology 3 credits
EE215 Research Methodology | 3 credits |
Block 2.5 Capstone project or Seminar 3 credits with 3 options:
2.5.1) EE490 Seminar in Economics | 3 credits or |
2.5.2) EE470 or EE4x9 Seminar in Specific Sub-Field Economics | 3 credits or |
2.5.3) EE500 Honors Thesis | 3 credits [1] |
Minor 1 Finance
Students must take 24 credits of Minor Area Study. To graduate with a Finance minor, at least 21 credits from the 24 credits enrolled in minor area subjects must meet the requirements listed in the table below, with a grade point average of at least 2.00.
Minor 2 Marketing
Students must take 24 credits of Minor Area Study. To graduate with a Finance minor, at least 21 credits from the 24 credits enrolled in minor area subjects must meet the requirements listed in the table below, with a grade point average of at least 2.00.
Course code / Course Title | Category | Credits | Requirements | MK211 Consumer Behavior | Compulsory for Marketing Minor | 3 credits | Receive at least C
for each course
|
|---|---|---|---|
MK312 Brand Strategic | 3 credits | ||
BA291 Business in a Changing World | 3 credits | Receive A, B+, B, C+, C, D+, D
| |
MK201 Principles of Marketing | 3 credits | ||
MKXXX (Choose one from MK elective courses) | Electives for Marketing Minor
| 3 credits | |
MKXXX (Choose one from MK elective courses) | 3 credits | ||
MKXXX (Choose one from MK elective courses) | 3 credits | ||
Choose any subjects listed as Minor Area Study course and fulfill the 24 credits requirement for Minor Area Study | Electives for Minor Area Study | 3 credits | Receive A, B+, B, C+, C, D+, D
|
Course code / Course Title | Category | Credits | Requirements | FN211 Financial Mathematics and Statistics | Compulsory for Finance Minor | 3 credits | Receive at least C
for each course
|
|---|---|---|---|
FN311 Financial Management | 3 credits | ||
FN312 Investments | 3 credits | ||
AC201 Fundamental Accounting | 3 credits | Receive A, B+, B, C+, C, D+, D
| |
BA291 Business in a Changing World | 3 credits | ||
FN201 Business Finance | 3 credits | ||
FNXXX (Choose one from FN elective courses) | Electives for Finance Minor
| 3 credits | |
Choose any subjects listed as Minor Area Study course and fulfill the 24 credits requirement for Minor Area Study | Electives for Minor Area Study | 3 credits | Receive A, B+, B, C+, C, D+, D
|
Minor 3 Free-cluster
With no more than 2 fields of studies, students can mix and match any Minor Area Study courses being offered by B.E. international program, and count the credits towards 24 credits to obtain the free-cluster minor degree.
[1] Major Area subjects, General Education courses and EE-subjects are NOT classified as Minor Area subjects. See the classification in the Course Catalog section.
General Education Courses
TU101 | Thailand, ASEAN, and the World Category: Compulsory Course for General Education World and Society | 3 (3-0-6) |
TU122 | Law in Everyday Life Category: Compulsory Elective Course for General Education Course Description: To study general aspects of law as correct patterns of human conduct in society. To equip learners with basic principles of public law (rules of law), and its values which are associated with citizens moral core. To provide basic knowledge in public law and private law, involving the issues of rights and duties, dispute settlement, Thai Justice procedures, the usage and interpretation of law principles, with an emphasis on case studies in our daily lives. World and Society | 3 (3-0-6) |
TU106 | Creativity and Communication Category: Compulsory Course for General Education Esthetic and Communication skills: | 3 (3-0-6) |
TU116 | Man and Arts : Visual Art, Music and Performing Arts Category: Compulsory Elective Course for General Education Course Description: This course is a study of art in relation to its function and the development of people, society and environment by focusing on various creative works, such as visual arts, music and performing arts, depicting the culture and perception of mankind. The course also aims to instill learners with real awareness of art values through personal experience, and also the appreciation of the aesthetic values of creative works. An emphasis is placed upon the influence of art on Thai values and the Thai way of life. Esthetic and Communication skills | 3 (3-0-6) |
TU103 | Life and Sustainability Category: Compulsory Elective Course for General Education Science, Mathematics and Technology | 3 (3-0-6) |
TU107 | Digital Skill and Problem Solving Category: Compulsory Elective Course for General Education Science, Mathematics and Technology | 3 (3-0-6) |
EL115 | English Communication for Careers Category: Compulsory Elective Course for General Education Course Description: Development of language and communication skills for careers. Strategies for presentations, networking, persuading, meetings, public relations, and negotiations. Study of social and business etiquette in professional contexts. Wellbeing and Future skills | 3 (3-0-6) |
EL295 | Academic English and Study Skills 1 Category: Compulsory Elective Course for General Education Wellbeing and Future skills | 3 (3-0-6) |
TU108 | Self Development and Management Category: Compulsory Elective Course for General Education Wellbeing and Future skills | 3 (3-0-6) |
TU100 | Civic Engagement Category: Compulsory Course for General Education Social Services and Practical Learning | 3 (3-0-6) |
Major Area Study Courses
EE400 | Seminar for Honor Thesis Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): (a) EE215 and (b) a minimum of three 400-level (or above level) economics Course and (c) having earned a cumulative GPA of 3.25 or higher at the beginning of the semester enrolled Course Description: Students choose research topics, write research proposals based on research methodology, and prepare and present honor thesis proposals with the approval of honor thesis advisors and honor thesis committee appointed by the Faculty of Economics.
Note: This course is offered only in the first semester of each academic year General Course for Major Area Study | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE490 | Seminar in Economics Category: Capstone Project Prerequisite(s): (a) EE215 (b) a minimum of four 400 level (or the above level) courses in the field Course Description: Seminar and Selection of research topics; development of stages of research; data collection and analysis, report writing under the supervision of the lecturer. General Course for Major Area Study | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE500 | Honor Theis Category: Capstone Project Prerequisite(s): (a) EE400 and (b) having earned a minimum cumulative GPA of 3.25 at the beginning of the semester enrolled, and with the consent of the assigned advisor. Course Description: Students conduct research and write their theses under the supervision and guidance of their thesis advisor and present honor thesis with the approval of honor thesis advisors and honor thesis committees appointed by the Faculty of Economics. General Course for Major Area Study | 3 (3-0-6) |
EL241 | English for Economists 1 Category: Compulsory Course for Major Area Study Course Description: Development of language skills in English for economics through lectures, reading, and discussion of contemporary issues. Practice and use of relevant vocabulary and study skills including note taking, paraphrasing and group discussions of basic economic issues. Skills development in describing economic trends, making predictions, and conducting economic debates. General Course for Major Area Study | 3 (3-0-6) |
EL341 | English for Economists 2 Category: Compulsory Course for Major Area Study Prerequisite(s): EL241 Course Description: Advanced English language practice in speaking, reading, listening and writing related to the field of economics. Practice in presenting opinions of current global events through group discussions, written reports and academic presentations. General Course for Major Area Study | 3 (3-0-6) |
MA216 | Calculus for Social Science 1 Category: Compulsory Course for Major Area Study Course Description: Limits and continuity of one variable functions, derivatives of algebraic functions and transcendental functions, implicit differentiation, higher order derivatives, Rolles theorem, the mean value theorem, applications of the derivative for determining limits and maximum and minimum of functions, differentials and its applications, antiderivatives, indefinite integrals and integration, definite intergrals and applications of area solving, functions of several variables, limits and continuity of functions of several variables, partial derivatives, the chain rule, total differential and its applications. Remark 1: No credit for students who are currently taking or have earned credits of MA111 or MA211 or MA218 or AM101. General Course for Major Area Study | 3 (3-0-6) |
ST 216 | Statistics for Social Science 1 Category: Compulsory Course for Major Area Study Course Description: Introduction to descriptive statistics; index numbers; unconditional and conditional probability; random variables and probability distribution; unconditional and conditional expectations; elementary sampling and sampling distribution; estimation and hypotheses testing for one population; statistical package results interpretation. Remark 1: No credits for students who passed or studying TU155 General Course for Major Area Study | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE301 | History of Thai Economy Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): – Course Description: Studying the evolution of Thailands economic system. The study focuses on examining the development of Thailand’s economic and social structure, while also investigating the roles of the state in the economy. The study links the changes in the Thai economy to the related economic, political, and social factors, both at the national and global levels. Field : 0 Political Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE302 | History of World Economy Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Course Description: Analyzing the history and development of world capitalism. The importance of the world economy is emphasized by selected topics such as the birth of capitalism, the Industrial Revolution, colonization, the Great Depression of the 1930s, the collapse of the Soviet Union, the development of Chinese and East Asian economies, the Oil Crises, and the World Financial Crises. Field : 0 Political Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE401 | Political Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): a) EE210 or b) EE211 and EE212 or c) EE213 and EE214 Course Description: Analyzing the development of capitalism. Theories and methodology of different schools of Economic thought from classical political economics to Karl Marx ‘ s political economics, post-Marxist political economics. Field : 0 Political Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE402 | Institutional Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): a) EE210 or b) EE211 and EE212 or c) EE213 and EE214 Course Description: Studying the development of institutional economics thought. Analyzing how institutions shape the incentives of economic agents, and how this influences socioeconomic outcomes. Examining factors contributing to the formation and demise of institutions, transactional costs, and changes within institutions. Using mainstream Economics to analyze the political market structure, political phenomena, and rent-seeking behavior as exercised by government bodies. Studying how Special Interest Groups (SIGs) impact economic policies. Field : 0 Political Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE403 | Law and Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): a) EE210 or b) EE211 and EE212 or c) EE213 and EE214 Course Description: Thailand ‘ s Legal System. The relationship between law, economy, and politics. Applying economic theory to analyze reasons for the existence of property rights, civil, and commercial law. The effects of law on economic behavior and on economic outcomes. Field : 0 Political Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE404 | History of Economic Thought Category: Compulsory Elective Course for Major Area Study Prerequisite(s): a) EE210 or b) EE211 and EE212 or c) EE213 and EE214 Course Description: Studying philosophical foundations, main ideas of different schools of economic thoughts, and debates among economists from past to present. Studying socio-economic and important events in history that influence economic ideas. Field : 0 Political Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE406 | Contemporary Economic Issues Category: Compulsory Elective Course for Major Area Study Prerequisite(s): EE211 and EE212 Course Description: This course is a general introduction to the subject matter and methods of economics, through the investigation of specific contemporary economic issues such as economic growth, inequality, poverty, and environmental deterioration. The focus also is on how economists address these issues. Field : 0 Political Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE409 | Seminar in Political Economics and Economic History Category: Capstone Project Prerequisite(s): Having completed at least two 400-level (or the above level) courses in the field of Political Economics and Economic History, excluding EE400, EE404, EE406 and EE500. Course Description: Seminar and research on specific topics in Political Economics and Economic History under the supervision of the lecturer. Field : 0 Political Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE501 | Selected Topics in Political Economics 1 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Studying selected topics in Political Economics and Economic History to be announced later. Field : 0 Political Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE502 | Selected Topics in Political Economics 2 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Studying selected topics in Political Economics and Economic History to be announced later. Field : 0 Political Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE210 | Introductory Economics Category: For Students who are not Economics major only Course Description: This course introduces the economic method of thinking to better understand real-world decision-making and improve analytical skills to better understand business and policy concerns. The fundamentals of modern economics, the general principles of microeconomics and macroeconomics, are introduced. Microeconomics covers how to apply the fundamental economic principles that explain why individuals and businesses make decisions with limited resources. The interactions of supply and demand in market operations are covered, as well as a variety of market structures ranging from monopoly to perfect competition. Furthermore, the course explores different sorts of failures and how government intervention policies might increase social welfare. Microeconomics covers how to apply the fundamental economic principles that explain why individuals and businesses make decisions with limited resources. The interactions of supply and demand in market operations are covered, as well as a variety of market structures ranging from monopoly to perfect competition. Furthermore, the course explores different sorts of failures and how government intervention policies might increase social welfare. Remark 1: For non-Economics majors only; credits will not be awarded to students who are taking or have completed EE211 or EE212 or EE213 or EE214 Field : 1 Economics Theory | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE211 | Principles of Microeconomics Category: Compulsory Course for Major Area Study Prerequisite(s): – Course Description: The course covers the principle microeconomic theories for making decisions under scarcity. The fundamentals of supply and demand, as well as their determinants, are established in the introduction to consumer and producer theories. Supply and demand collaborate to establish pricing and resource allocation efficiency through two basic market structures: monopoly and perfect competitive markets, and competitive factor markets. The principles and effects of market failures are also introduced. Field : 1 Economics Theory | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE212 | Principles of Macroeconomics Category: Compulsory Course for Major Area Study Course Description: The course covers the principle macroeconomic theories that explain how the economy works at a macro level and the mechanisms via which policies might intervene. The course covers the most important macroeconomic measurements and issues. The accelerator principle, money markets, the theory of supply and demand for money, the joint equilibrium model of product and money markets (IS-LM model), the balance of payments, and fiscal and monetary policy as means of stabilizing an economy are all discussed. The concept of collecting and managing Thai macroeconomic data for the purpose of analyzing economic situations is introduced. Field : 1 Economics Theory | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE213 | Introductory Microeconomics Category: For Students who are not Economics major only Course Description: The course provides a practical understanding of the core economic principles that explain why consumers and companies make their decisions given scarce resources. The topics include the interactions of supply and demand of market operations, through wide-range market structures, ranging from monopoly to perfect competition. Moreover, the course also explains types of failures, in which the role of government intervention policy can improve social welfare. Remark 1: For students who are not Economics majors Field : 1 Economics Theory | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE214 | Introductory Macroeconomics Category: For Students who are not Economics major only Course Description: The course will provide you a practical understanding of the fundamental macroeconomic theories that explain how the economy functions and how macroeconomic policies affect it. The course will cover key macroeconomic measurements, problems, and policy performance, as well as the determinants of national income, employment, and price level, the role of monetary policy and the banking system in stabilizing the economy, and the role of monetary and fiscal policies in stabilizing the economy. The balance of payments, foreign currency market and exchange rate determination, and the use of economic indicators to understand economic circumstances are all covered in the international economics part. Remark 1: For students who are not Economics majors Field : 1 Economics Theory | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE215 | Research Methodology Category: Compulsory Course for Major Area Study Prerequisite(s): EE211 and EE212 and EE325 (or EE425) Course Description: Study methods of conducting research and writing report in economics by studying the meaning and objectives and economic research characteristics. Study the composition and process of conducting research consisting of topic selection. Defining Objectives and Scopes setting and testing hypotheses for the use of educational theories and methods; Various statistical sources, both primary and secondary. preparation of research projects, proposals, data processing, and analysis and writing of research reports Remark 1: Evaluation is based on Satisfactory ‘ (S)/ ‘ Unsatisfactory ‘ (U) grading. Remark 2: This course is only for economics students. Field : 1 Economics Theory | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE311 | Microeconomic Theory Category: Compulsory Course for Major Area Study Prerequisite(s): EE211 (or EE213) and MA216 (or MA211) Course Description: Consumer behavior focuses on indifference curve analysis, intertemporal consumption, consumption, and risks. Theory of production and cost, the birth of the firm using information cost, structure and behavior of imperfectly competitive markets which are a monopoly, monopolistic competition, and duopoly markets. Introduction to game theory. Price setting in practice. Price determination in factor markets, general equilibrium analysis, welfare Economics, market failures ,and measures to correct. Field : 1 Economics Theory | 4 (4-0-8) |
EE312 | Macroeconomic Theory Category: Compulsory Course for Major Area Study Prerequisite(s): a) EE211 and EE212 or b) EE213 and EE214 Course Description: The course discusses the economy’s mechanism using a general equilibrium approach, which proposes appropriate government policies to stabilize and boost economic growth. Classics, New Classics, Keynesian, and New Keynesian school of thinking are all used to create appropriate policies. The role of how the labor market perceives and responds to information in determining the character of aggregate supply and the Phillips curve is examined for the closed economy. The static and dynamic elements of aggregate supply and demand interactions are investigated. Furthermore, the microeconomics foundation is utilized to investigate how agents react to one another, to policies, and to the economy’s growth. The model of joint equilibrium (IS-LM-BP) in product markets, money markets, and foreign exchange markets for an open economy. Field : 1 Economics Theory | 4 (4-0-8) |
EE411 | Microeconomic Analysis Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 and EE320 (or EE421) Course Description: Microeconomic theory with an emphasis on utilizing mathematical tools to analyze economic issues such as consumer behavior, revealed preferences, intertemporal consumption, consumption under risk, theories of production and cost, market structures and behavior of markets, and other topics that the lecturer finds suitable. Field : 1 Economics Theory | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE412 | Macroeconomic Analysis Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE312 and EE320 (or EE421) Course Description: Macroeconomic theory with an emphasis on utilizing mathematical tools and dynamic framework to analyze economic issues, such as, general equilibrium and welfare analysis in modern Macroeconomics, analysis of long-term growth, analysis of short-term growth and fluctuations both theoretically and empirically, roles of government in the economy, modern concepts for macroeconomic policy analytical frameworks, and the other topics that the lecturer finds suitable. Field : 1 Economics Theory | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE415 | Game Theory Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 and EE320 (or EE421) Course Description: The application of game theory with complete and incomplete information including strategic games, Nash Equilibrium, mixed-strategies equilibrium, extensive games, subgame perfect equilibrium, Bayesian games, extensive games of incomplete information, and other topics that the lecturer finds suitable. Field : 1 Economics Theory | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE416 | Behavioral Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Concepts and frameworks in behavioral economics including a comparative study of models for decision under uncertainty between mainstream economics and behavioral economics, empirical evidence that support behavioral economics, models that incorporate psychological and sociological factors for consumer and social behaviors, and other topics that the lecturer finds suitable. Field : 1 Economics Theory | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE511 | Selected Topics in Economic Theory 1 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Studying topics in Economic Theory to be announced later. Field : 1 Economics Theory | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE512 | Selected Topics in Economic Theory 2 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Studying topics in Economic Theory to be announced later. Field : 1 Economics Theory | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE320 | Introductory Mathematical Economics Category: Compulsory Course for Major Area Study Prerequisite(s): a) EE211, EE212 and MA216 (or MA211) or b) EE213, EE214 and MA 216 (or MA 211) Course Description: Applying mathematical concepts and tools such as functions, equations, matrices, univariate and multivariate differential calculus, constrained and unconstrained optimization, and basic integral to understand the relationship between different economic variables and explain concepts of Microeconomic theory and Macroeconomic theory. An emphasis will be placed on relationships between total, average, and marginal functions, the analyses of elasticity, market equilibrium, impacts of taxation, and the basic input-output model. Remark 1: Credits will not be awarded to students who are taking or have completed EE421 Field : 2.1 Quantitative Economics: Mathematical Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE421 | Mathematical Economics 1 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): MA217 (or MA212) and having completed or currently taking EE311 Course Description: The application of matrices, Jacobian determinants, derivatives, partial derivatives and optimization, with and without constraints, to explain theories in Microeconomics and Macroeconomics, such as the theory of consumer behavior, the theory of production, equilibrium in goods and factor markets, equilibrium of national income in product and money markets, international trade, comparative static equilibrium analysis, the input-output model, determination of maximum-minimum point and duality of linear programming. Field : 2.1 Quantitative Economics: Mathematical Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE422 | Mathematical Economics 2 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE421 and having completed or currently taking EE312 Course Description: Applying mathematical tools such as integral calculus, differential equations, difference equations, phase diagram, and dynamic optimization such as optimal control theory and dynamic programming to explain dynamic economic phenomena as well as to locate the time and stability of variables in the context of both Microeconomics and Macroeconomics. The study of dynamic input-output models is also covered. Field : 2.1 Quantitative Economics: Mathematical Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE423 | Data Analytics Programing for Economists Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE320 and EE325 Course Description: This course is an introduction to programming such as Python or R to undertake analysis of data. It is aimed at preparing the knowledge of computers and programming for analyzing data in economics and finance. The course goes on to cover data cleansing, the manipulation of data, and basic statistics in explaining the data. The course will also cover how data can be visualized and the knowledge of how the data can be transformed and reduced to its dimension. Field : 2.1 Quantitative Economics: Mathematical Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE424 | Data Science for Economics and Finance Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE423 Course Description: This course will cover topics that range between Supervised (predictive) and Unsupervised Machine Learning methods. Examples include Regression and K Nearest Neighbors, Classification, Dimensionality Reduction, Decision Trees and Random Forests, Principal Component Analysis and Clustering Analysis. All computing in this course will be conducted in R or Python. The course will focus on the case studies with applications to data sets used to study economic and finance phenomena. Field : 2.1 Quantitative Economics: Mathematical Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE325 | Introductory Econometrics Category: Compulsory Course for Major Area Study Prerequisite(s): EE211 (or EE213), EE212 (or EE214), MA216 (or MA211) and ST216 (or ST211) Course Description: Apply basic concepts in econometrics, including; linear estimation methods and problems with remedial technique i.e. Multicollinearity, Heteroscedasticity, Autocorrelation, Specification error, Identification, solving endogeneity problem using Instrumental Variable (IV) technique, and Logit model. Practical applications of all topics are mainly emphasized, as well as, how to choose the appropriate tool for an empirical study and interpretation of the estimated results obtained from econometric software. Remark 1: Credit will not be awarded to students who are taking or have completed EE425) Field : 2.2 Quantitative Economics: Econometrics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE425 | Econometrics 1 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE211 (or EE213), EE212 (or EE214), MA216 (or MA211) and ST216 (or ST211) Course Description: Applying statistical methods and economic theories to analyze economic data, including simple and multiple regressions; estimation using the ordinary least squares (OLS) hypothesis testing; and dummy variable. This course also examines various problems in regression models, including Multicollinearity, Heteroscedasticity, Autocorrelation, Specification Error, Stochastic Regressors; and some advanced topics in regression method such as Generalized Least Squares (GLS) estimation, System of regressions and Seemingly Unrelated Regression (SUR), Simultaneous Equation System and solving Endogeneity problem with instrumental variables. Trainings in econometrics softwares. Field : 2.2 Quantitative Economics: Econometrics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE426 | Econometrics 2 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE425 Course Description: This course covers Maximum Likelihood estimation, panel data model, limited dependent variable model. Field : 2.2 Quantitative Economics: Econometrics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE427 | Time Series Analysis Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE425 Course Description: This course covers Maximum Likelihood estimation and the introduction to time series data focusing on univariate time series, AR, MA, ARMA, ARIMA, forecasting, ARCH, GARCH, EGARCH, VARs, cointegration and error correction model, and VECM. Field : 2.2 Quantitative Economics: Econometrics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE521 | Selected Topics in Quantitative Economics 1 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Study of topics in Quantitative Economics to be announced later. Field : 2.2 Quantitative Economics: Econometrics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE522 | Selected Topics in Quantitative Economics 2 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Study of topics in Quantitative Economics to be announced later. Field : 2.2 Quantitative Economics: Econometrics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE431 | Economics of Financial Markets and Financial Institutions Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Money and capital markets at a micro-level; Financial assets, risks, and risk-bearing; The theory of equilibrium pricing of financial assets; Interest rate determination and structure of interest rates; Asymmetric information in financial markets; The study of financial institutions; Risk management of financial institutions; Behavior of financial institutions; Regulating financial institutions, Other contemporary issues and recent developments in financial system. Field : 3 Monteray and Financial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE432 | Monetary Theory and Policy Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE312 Course Description: The role of money in the economy; studying monetary policys goals, tools, policy implementations, Transmission mechanisms of Monetary policy; Monetary policy and business cycles; monetary policy framework, exchange rate targeting and inflation targeting; The role of the Central Bank; The interaction between monetary and fiscal policies; The role of monetary policy in the open economy; Other contemporary issues and recent developments related to monetary policy Field : 3 Monteray and Financial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE433 | Asset Pricing Theory Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 and EE320 (or EE421) Course Description: Study concepts and frameworks of asset pricing theory in the intermediate level; the theory of choice under uncertainty; classical asset pricing theory in the discrete time such as the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), The Arbitrage Pricing Theory (APT), and The Consumption Capital Asset Pricing Model (C-CAPM); Empirical puzzles in asset pricing/returns and proposed resolutions in the literature. Field : 3 Monteray and Financial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE434 | Behavioral Finance Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 and EE325 (or EE425) Course Description: Study concepts and frameworks of behavioral economics that are used to explain observations in the financial sector. Topics of the subject include the Prospect Theory and its implications for investment behaviors, empirical evidences in the financial sector that support the idea of behavioral economics, models that incorporate psychological and sociological factors in explaining asset returns, or other related topics that the lecturer finds suitable. Field : 3 Monteray and Financial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE435 | Introductory Financial Econometrics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE325 (or EE425) and EE431 (or EE432) Course Description: The application of econometrics method to finance and macroeconomics data. Applications of regression models. Applications of Probit-Logit model to financial risk assessments. Characteristics and properties of time-series based financial data. Univariate Time-Series Model. Regression with the long-run relationship and short-run dynamics. Volatility Model. Training in statistical software, emphasizing the application of tools suitable for research and study in finance-related issues. Field : 3 Monteray and Financial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE439 | Seminar in Monetary and Financial Economics Category: Capstone Project Prerequisite(s): Having completed at least two 400-level (or the above level) courses in the field of Monetary and Financial Economics. Course Description: Seminar and research on topics in Monetary and Financial Economics under the supervision of the lecturer. Field : 3 Monteray and Financial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE531 | Selected Topics in Monetary and Financial Economics 1 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Study of topics in Monetary and Financial Economics to be announced later. Field : 3 Monteray and Financial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE532 | Selected Topics in Monetary and Financial Economics 2 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Study of topics in Monetary and Financial Economics to be announced later. Field : 3 Monteray and Financial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE340 | Introductory Public Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): a) EE210 or b) EE213 and EE214 or c) EE211 and EE212 Course Description: This course introduces students to the basic concepts of public finance, including the principles of the public sector and welfare economics. It provides an overview of the role of government and shows the interaction between the public sector, fiscal institutions, and the private economy. Empirical case studies illustrating public policy-making in practice will also be covered. Remark 1: Credits will not be awarded to students who are taking or have completed any 400-level courses in this field. Field : 4 Public Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE341 | Local Public Finance Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): a) EE210 or b) EE211 and EE212 or c) EE213 and EE214 Course Description: This course critically examines local government fiscal systems. Major topics include understanding and determining an appropriate division of fiscal responsibilities among levels of government or expenditure assignment; criteria for local revenue assignment including local levied revenue, central allocation revenue, and intergovernmental finance. The course focuses on economic analysis, but attention is also given to political, institutional, and cultural considerations that are critical for effective policy design and implementation. Remark 1: Credits will not be awarded to students who are taking or have completed any 400-level courses in this field. Field : 4 Public Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE441 | Public Economics 1 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE212 (or EE214) and EE311 Course Description: The course covers the role of the government in the allocation of resources for the public sector of the economy. Topics covered will include government (national and local) outlays and budgets, the provisions of public goods and the regulation of market failures. The role of the governments budget processes in providing macroeconomic stability, growth and income redistribution. This analysis also includes fiscal decentralization (the budget allocation of local governments). The application of these tools to selected contemporary topics such as social security, cost-benefit analysis, healthcare and education financing will also be covered. Field : 4 Public Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE442 | Public Economics 2 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE212 (or EE214) and EE311 Course Description: The course analyses the structure and composition of government (national and local) revenue, through analysis of tax burden and incidence, and tax effects upon efficiency and equity. The course looks at the empirical effects of tax policies on the economy as a whole, and various individual behaviors such as decisions about work and leisure, tax avoidance and evasion, investment, savings and consumption. The analysis also includes the effects of deficit finance and fiscal decentralization (local revenue, grants and local debt). The application of these tools to selected contemporary topics (social security, healthcare and education financing). Additionally, the class will explore the politics and economics of tax reforms. Field : 4 Public Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE443 | Public Choice Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE212 (or EE214) and EE311 Course Description: This course introduces students to the principles of Public Choice Economics, also known as Politics without the Romance. Using the same core assumptions about Homo Economics that guides our analysis of how individuals and firms act and interact in a market, this class will then explore how those same people act in the public sphere. Topics covered will include the paradox of voting, the voting systems and institutional incentives, bureaucracies, rent-seeking, constitutional economics, and more. Both international and Thai case studies will be used to illustrate the limits of government intervention, and the dangers of government failure. Field : 4 Public Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE444 | Economics of Corruption Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Study of corruption by using economic analytical framework both theoretical and empirical methodology. Topics include definition and coverage of corruption, causes of corruption, economic consequences of corruption both on micro and macro levels, public policies and measures in combating corruption. Moreover, roles of private sector, civic society, and international organizations in tackling with corruption including case studies will be discussed. Field : 4 Public Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE449 | Seminar in Public Economics Category: Capstone Project Prerequisite(s): EE441 and EE442 Course Description: Seminar and research on topics in Public Economics under the supervision of the lecturer. Field : 4 Public Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE541 | Selected Topics in Public Economics 1 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Study of topics in Public Economics to be announced later. Field : 4 Public Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE542 | Selected Topics in Public Economics 2 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Study of topics in Public Economics to be announced later. Field : 4 Public Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE351 | International Economic Cooperation and Trade Negotiations Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): a) EE210 or b) EE211 and EE212 or c) EE213 and EE214 Course Description: All levels of economic cooperation agreements (bilateral, regional, and multilateral ones) are covered. The lecture starts with motivation, types, scope, governance mechanism, and its impact. The discussion will also cover the role of international organizations in economic cooperation and economic-related dispute settlements. Field : 5 International Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE451 | International Trade Theory and Policy Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Both international trade theory and trade policy practices are covered in this subject. Relevant international trade theories will be discussed, together with the hypothesized consequence and its empirical support. Both tariff and non-tariff trade policy measures are examined. In the latter, both traditional (e.g. quota, local content requirements) and new forms (sanitary and phyto sanitary, technical requirement) of non-tariff measures are covered. Discussion in the subject also covers free trade agreements and international production sharing, both of their impacts. Field : 5 International Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE452 | International Monetary and Financial Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE312 Course Description: The Course focuses on balance of payments, exchange rate, and their interaction with other macroeconomic variables. It begins with basic features of balance of payment including definition, components and its dynamics. That of exchange rate covers its basic concept (measurement, its determinants, and its equilibrium). Both balance of payments and exchange rate interacting with other macroeconomic variables are discussed through open-macro economy model. Note other key macroeconomic variables include output, interest rate, and inflation. It will cover macro-economic policy regimes such as monetary policy regime (i.e. inflation targeting), and exchange rate policy regime. Recent development in international monetary and finance economics will be integrated into the Course, e.g. Asian financial crisis, Sub-prime crisis, policy coordination, digital currency. Field : 5 International Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE459 | Seminar in International Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE451 and EE452 Course Description: Seminar and research on topics in International Economics under the supervision of the lecturer. Field : 5 International Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE551 | Selected Topics in International Economics 1 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Study of topics in international Economics to be announced later. Field : 5 International Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE552 | Selected Topics in International Economics 2 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Study of topics in international Economics to be announced later. Field : 5 International Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE361 | Economics of Asian Countries and Others Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): a) EE210 or b) EE211 and EE212 or c) EE213 and EE214 Course Description: Economic development in Asia and/or selected countries according to the lecturers announcement. The transformation of their economic structure. The roles of public and private institutions along with other economic, social, and political factors that contribute to their economic changes. The relationship between these economies and the world and Thai economies. Field : 6 Development Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE362 | Contemporary Issues in ASEAN Countries Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): EE211 and EE212 and having completed at least 60 credits Course Description: The contemporary issues in ASEAN countries. Study various aspects of the overall ASEAN or each countrys economy i.e. socio-economic issues, politics, businesses, trade and investment, economic development, finance, etc. Roles of regional organizations, economic interconnection across countries, and linkages with the Thai economy. The learning methods are the active and problem-based learning with some experienced guest speakers, discussion, and field trips visiting public and/or private organization(s) in Thailand and another ASEAN member country, according to the lecturers announcement. Field : 6 Development Economics | 6(6-0-9) |
EE363 | Gender Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): a) EE210 or b) EE211 and EE212 or c) EE213 and EE214 Course Description: Evolution of male and female roles in the economic system. Theories of family formation. Differences in gender-related time allocation for market and non-market activities. Supply and demand factors determining gender-related differences in occupation and income, and gender roles switching in occupation. Roles of female in socio-economy and politics. Different effects of policies or welfare programs on gender. Gender in the aging economy. Effects of economic crisis on family and gender in the labor market. Roles of the LGBT in the economy. Gender equality in international criteria, and other interesting issues. Field : 6 Development Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE364 | Economics of Local Development Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): a) EE210 or b) EE211 and EE212 or c) EE213 and EE214 Course Description: Dynamics of local development in rural and urban areas. Economic and social theories regarding communities and collective action of people in communities. Interactions between livelihoods, natural resource capital, cultural and ethnic factors, and their influences on local farm and non-farm economic activities. Responses and adaptation of local communities to development policies. Roles of actors, such as community leaders, government officers, local administrative organizations, academics, and non-governmental organizations in local development. Analysis of capacities and limitations of local communities for collaboration in the allocation of resources and conducting economic activities. Sustainable development in the context of local development. Alternative approaches for local development such as incorporating with social entrepreneurs. Field : 6 Development Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE365 | Local Study and Development Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): EE364 Course Description: Field study of key development issues in the selected local area. Analyzing the socio-economic factors, resources, and roles of the stakeholders involving the issues. The action-based learning is supervised by the lecturer. Remark 1: Theory and Practice hours are at least 270 hours during the summer session. Field : 6 Development Economics | 6 (6-9-9) |
EE460 | Thai Economy Category: Compulsory Elective Course for Major Area Study Prerequisite(s): EE311 and EE312 Course Description: Thai economic structure and how it changes. Economic performance in terms of development and growth. The countrys resolutions for poverty eradication, income distribution, economic stability, and quality of life. The process of economic policy formulation in Thailand. Monetary and fiscal policy implementation. National economic and social development strategies and sectoral economic strategies such as the industrial agricultural development. The relationship between the Thai and world economy, the international economic order, and international organizations such as the World Bank, International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the World Trade Organization (WTO). Field : 6 Development Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE461 | Development Microeconomics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Concepts and measurements of poverty and inequality. The theories of justice for analyzing public policies related to these issues. Microeconomic theories related to household decisions and behaviors, as well as market failures in developing countries. Public policies on development issues such as health; education; population; workforce allocation of households in agriculture and non-agriculture sectors, as well as formal and informal sectors; migration; entrepreneurship of the households; households financial and risk management tools; microfinance; innovations and other interesting issues related to poverty reduction, etc. Field : 6 Development Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE462 | Development Macroeconomics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE312 Course Description: Analyzing economic issues in the macroeconomics of developing countries. These include theories and thoughts explaining economic growth; relationship between economic growth and poverty; income distribution; development policies of different countries in the past; and the impact of short-term macroeconomic policies such as stabilization policies, monetary and fiscal policies, exchange rate management, and various factors affecting economic growth e.g. international trade and investment, capital flow, financial crises, social welfare, and structural change. Field : 6 Development Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE463 | Globalization and International Development Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): a) EE211 and EE212; or b) EE213 and EE214 Course Description: Concept and development of globalization in the context of after World War II. Formation of the New International Economic Order (NIEO). Global organizations. Multinational corporations. International cooperation. The political economy of dependency. Debates on the contribution and impacts of globalization on the local economy. Contemporary transnational development issues. Roles of international development organizations e.g. the United Nations, World Bank, International Monetary Fund (IMF), etc., in bridging the global north and the global south or within the south countries through official development assistance (ODA), development loan, or development projects. Analysis of patterns, factors of success, and failures of past international development projects. Basic techniques for development project evaluation. Field : 6 Development Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE464 | Urban and Regional Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311, EE212 (or EE214), and EE325 (or EE425) Course Description: Topics in urban economics and/or regional economics proposed by the instructors. Examples of possible topics are urbanization, urban land and housing market, urban public goods and service, sustainable and inclusive city development policies, new economic geography, location and cluster theories, regional growth and inequality, basic spatial analysis, geographical information system (GIS) and using GIS related program, special economic zones, current policy issues in urban and regional development, etc. Field : 6 Development Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE465 | Sustainable Development Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE212 (or EE214) and EE311 Course Description: Development of sustainable development approach under context of socio-politico-economic development at different levels. Sustainable development crises at global level and in Thailand. Definitions and fundamental ideas regarding Sustainable Development and contemporary debates. Other approaches related to sustainable development and their critiques, such as Gross National Happiness (GNH), Sufficiency Economy Philosophy, Green Growth, etc. Economic theories related to sustainable development, such as the analysis of externalities, public goods, common-pool resources, ecological economics, Green Economy, and economic measures for sustainable development. Policies and indicators related to sustainable development at global level, particularly the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Challenges and obstacles to achieve sustainable development. Field : 6 Development Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE467 | Project Evaluation and Economic Valuation Techniques Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE212 (or EE214), EE311 and having completed at least one 400-level (or the above level) course in field 3 to field 9 Course Description: Study welfare economic foundations of economic project evaluation. Study project evaluation methodologies, including Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA), Cost Effectiveness Analysis (CEA) and Multi-Criteria Analysis (MCA); as well as project evaluation criteria, e.g., Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of return (IRR), etc. Study quantitative techniques for economic valuation, including market-based techniques, hedonic pricing method, travel cost method, contingent valuation method, choice modeling, benefit transfer, value of statistical life, etc. Field : 6 Development Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE468 | Integrated Public Economics, Development and Political Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 and having completed at least two 400-level (or the above level) courses in Political Economics or Public Economics or Development Economics. Course Description: The integration of theories and concepts in public economics, institutional economics, development economics, and political economy; Enhancing students ability to link and apply economic theories in this subject area to analyze situations and problems arising in Thailand or in the world economy; Encouraging students to learn through case studies of current situations, with the emphasis on causes, nature, and effects of the problems; Promoting students to use economic and related social science theories as tools to explain and find solutions to the problems; Supporting students to consider interactions between the focused economic or social phenomenon and political factors, i.e. state and characteristics of the state, political regime, institutional change, public policy process, as well as understand roles and influences of culture, history, geography, international politics and development; Analyze roles of market, state, communities and civil society organizations in solving the problems while take into account institutional factors underlying the economic and political structure. Field : 6 Development Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE469 | Seminar in Development Economics Category: Capstone Project Prerequisite(s): Having completed at least two 400-level (or the above level) courses in Development Economics, excluding EE460 and EE468. Course Description: Seminar and research on topics in Development Economics under the supervision of the lecturer. Field : 6 Development Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE561 | Selected Topics in Development Economics 1 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Studying topics in Development Economics to be determined later. Field : 6 Development Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE562 | Selected Topics in Development Economics 2 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Studying topics in Development Economics to be determined later. Field : 6 Development Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE470 | Seminar in Human Resources Economics Category: Capstone Project Prerequisite(s): Having completed at least a 400-level (or the above level) course in Human Resource Economics or any other economic fields (e.g. Field 4: Public Economics, Field 6: Development Economics) Course Description: Seminar and research on topics in human resource economics under the supervision of the lecturer. Field : 7.1 Human Resource Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE471 | Labor Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Studying the supply and demand of labor in the short-term and long-term, wage determinations as well as improving labor quality through education and human capital training. Labor migration, wage structure, wage differentials in the labor market, job search, unemployment, and the role of labor unions will be covered. The role of government in the labor market as employer or regulator. Social security, discrimination in the labor market will be discussed. Field : 7.1 Human Resource Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE472 | Economics of Population and Family Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Processes generate change in population and family size and structure through reproduction, death, and migration. Factors causing these changes. The impact of demographics and family variables on the economy at the micro and macro levels. The Economics of Marriage, the Economics of Household/Family, and the Economics of Aging will be included. Field : 7.1 Human Resource Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE473 | Economics of Education Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Principles of investment in education, measuring return on education, theory of human capital and choice theory explaining educational investment will be discussed. Principles of investment in on-the-job training, analyzing educational impact on key economic variables such as wages throughout the entire working period, growth in the wage rate, job switching, and expansion of the economy as a whole will be covered. Evaluating efficiency and equality in governmental budget allocation within the educational system. Field : 7.1 Human Resource Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE474 | Health Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 or EE312 Course Description: Economic thought about health and health care services. Supply of and demand for health care. Market failure in the health care market and government intervention. Health insurance, fiscal policy on public health, factors of health service production, and efficiency and equality in the health care system. Evaluation of health care projects, asymmetric information in health insurance, and health economics at the Macro level. Health service system reform in Thailand and abroad. Field : 7.1 Human Resource Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE571 | Selected Topics in Human Resource Economics 1 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Studying selected topics in Human Resource Economics to be determined later. Field : 7.1 Human Resource Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE572 | Selected Topics in Human Resource Economics 2 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Studying selected topics in Human Resource Economics to be determined later. Field : 7.1 Human Resource Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE375 | Applied Economics for Natural Resources and Environment Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): EE210 or EE211 or EE213 Course Description: The relationship between economic growth, natural resources allocation and environmental problems. Basic economic theories used for analysis and application in natural resources management and environmental problems. The roles of government, community, and business sectors to control and solve problems in natural resource and environmental exploitation at local, national, and global levels. Concept of sustainable development. Concept of environmental justice. Basic concepts and methodologies in economic valuation of natural resources and environment. Current issues in natural resource and environment. Remark 1: credits will not be awarded to students who are taking or have completed any 400-level courses in this subfield. Field : 7.2 Natural Resource and Environmental Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE376 | Economics of Climate Change Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): EE210 or EE211 or EE213 Course Description: Basic scientific knowledge of climate change. Greenhouse gas emissions and climate change mitigation. Concept of market failure and economic measures to support climate mitigation and technological development. Impacts of these measures on the economy, international trade, and investment. Economics of climate change adaptation. International climate negotiation and cooperation. Field : 7.2 Natural Resource and Environmental Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE475 | Natural Resource Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Economic theories and tools used for natural resource allocation. Concepts of scarcity and economic rent of natural resources. Allocation of natural resource among current users as well as intertemporal allocation. Market failure due to deficiencies in the property rights system. Government policies and tools for natural resource management and their impacts. Field : 7.2 Natural Resource and Environmental Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE476 | Environmental Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: The concepts of sustainable development, efficient production, efficient consumption and market failure. The concepts of efficiency and effectiveness of policies, measures, and tools to control and solve environmental problems. Environmental risk assessment. Economic valuation and environmental impact assessment of development projects. Concept of environmental justice. Issues related to international environmental cooperation and agreements, including the effects on trade and investment and current issues in environment. Field : 7.2 Natural Resource and Environmental Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE477 | Energy Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Factors influencing energy resource production, processing, transportation and demand. Substitution among different energy resources. The importance of energy to the economy and the impacts of energy on the environment. The energy market structure and prices of different types of energy, along with problems in global oil pricing and the role of OPEC. Governmental policy on the provision, production and use of energy, including price regulation and provision, production, and efficient use. The use of alternative energy to replace fossil fuel. International cooperation and agreements related to energy sector. Each topic will include the discussion of case studies from Thailand, in order to encourage better understanding of situation and problems in the Thai context. Field : 7.2 Natural Resource and Environmental Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE479 | Seminar in Natural Resources and Environmental Economics Category: Capstone Project Prerequisite(s): Having completed at least two courses from EE376 or EE475 or EE476 or EE477 Course Description: Seminar and research on topics in Natural Resources and Environmental Economics under the supervision of the lecturer. Field : 7.2 Natural Resource and Environmental Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE573 | Selected Topics in Natural Resources and Environmental Economics 1 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Studying selected topics in Natural Resource and Environmental Economics to be determined later. Field : 7.2 Natural Resource and Environmental Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE574 | Selected Topics in Natural Resources and Environmental Economics 2 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Studying selected topics in Natural Resource and Environmental Economics to be determined later. Field : 7.2 Natural Resource and Environmental Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE380 | Introduction to Industrial Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): EE210 or EE211 or EE213 Course Description: The importance of the economys industrial sector. Relationship between the industrial sector and other sectors, on the domestic and international level. Studying market structure, conduct, and competitiveness of the industrial sector. Government policy, the legal system, and their effects on industrial development. Remark 1: credits will not be awarded to students who are taking or have completed any 400-level courses in this field. Field : 8 Industrial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE381 | Economics of Transportation Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): EE210 or EE211 or EE213 Course Description: The role of transportation in the domestic and international economy. How transportation affects the location of businesses and production sites. Criteria and economic reasons for transportation pricing. Private and social costs related to transportation. How urban transportation is affected by expansion. Problems and policies related to investment in urban transportation. Field : 8 Industrial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE382 | Economics of Services Sector Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): a) EE210 or b) EE211 and EE212 or c) EE213 and EE214 Course Description: Key characteristics of service. Contribution of the service sector to the economy and economic development. Application of economic and business concepts in the analysis of selected service industries especially the tourism sector. Analysis and discussion of case studies in the service sector in various aspects. Field : 8 Industrial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE383 | Cultural Economics and Creative Economy Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): a) EE210 or b) EE213 and EE214 or c) EE211 and EE212 Course Description: Economic aspects of arts, cultural heritages, art creators and performers as well as creative economy; Economic evaluation on arts and cultural heritages; Economic development based on arts and culture heritages; Practical problems of arts and cultural heritage management; and Economic measures promoting artworks and creative economy. The importance of creativity and innovation in value creation and the role of creativity in business and the economy. Field : 8 Industrial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE481 | Industrial Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: This course studies the behaviors of firms under imperfectly competitive markets. It covers the structureconductperformance (SCP) paradigm, which examines the relationship among market structure, firms conduct, and their performance. It also covers firms decisions on operation, resource allocation, as well as firms strategic actions. Price theory and game theory will be used to analyze issues such as pricing, research and development, advertising, and firms decision under imperfect information. Competition in multi-sided markets and the importance of platforms. The role of competition policy in competition regulation. Field : 8 Industrial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE482 | Economics of Innovation and Industrial Development Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Economic theories related to science, technology, innovation, and industrial development. The importance of innovation and industrial development in the Thai economy. Evolution of Industrial Policy and Innovation Policy in Thailand, including developing new economic forms such as the Knowledge-based Economy, Digital Economy, and Industry 4.0. The role of government and private sector in science, technology, innovation, and industrial development. Concepts and tools for developing science, technology, innovation, and industrial development. Field : 8 Industrial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE483 | Economics of Regulation and Competition Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Study of regulatory theories, competition policies, together with their economic rationales. Study of approaches, methods, instruments and impact assessment of regulation and competition policies. Study of regulatory institutions, governance and performance. Study of case studies from the developed and developing countries. Field : 8 Industrial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE484 | Empirical Industrial Organization Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 and EE325 (or EE425) Course Description: The empirical approach in industrial economics and application of econometric analysis in industrial economics theory i.e., Estimation of demand and production functions, Measurement of market power, Analysis of firms strategic behavior, Vertical and horizontal competition, Firm’s entry decisions, contract, and learning. Measurement of firm performance by efficiency and productivity indicators. Field : 8 Industrial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE486 | Business Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Theories and tools are applicable for analysis of business problems and solutions, such as the application of economic concepts to forecast economic and industrial conditions, determination of business strategy, marketing, production, organization, human resource management, and decision-making. Field : 8 Industrial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE489 | Seminar in Industrial Economics Category: Capstone Project Prerequisite(s): Having completed at least two 400-level (or the above level) courses in field of Industrial Economics Course Description: Seminar and research on topics in Industrial Economics under the supervision of the lecturer. Field : 8 Industrial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE581 | Selected Topics in Industrial Economics 1 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Studying topics in Industrial Economics to be determined later. Field : 8 Industrial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE582 | Selected Topics in Industrial Economics 2 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Studying topics in Industrial Economics to be determined later. Field : 8 Industrial Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE390 | Introduction to Agricultural Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (300-level) Prerequisite(s): EE210 or EE211 (or EE213) Course Description: The role of agriculture in economic development. Structure and structural change of the agricultural economy. Production, market, and price of agricultural products. Agricultural institutions. The relationship between agriculture and natural resource and environmental problems. Agricultural development policies in Thailand. Field : 9 Agricultural Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE491 | Agricultural Production and Policy Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Explore economic theoretical concepts and related issues on agricultural production, such as cost of production, supply of agricultural products, agricultural productivity and efficiency, risk, technological change at the farm level, etc. Also explore public policies and institutions related to farmers and agricultural production, such as land tenure, credit system, cooperative system, cultural change, policy change affecting agricultural production, and other interesting contemporary issues. Field : 9 Agricultural Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE492 | Agricultural Marketing and Policy Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE311 Course Description: Explore economic theories and challenging issues related to agricultural markets throughout supply chain, such as agricultural products demand and supply, various types of elasticity of demand for agricultural product price adjustment in agricultural product market under different conditions including marketing, season, and roles of middlemen, etc. Also explore public policies and institutions related to domestic and international agricultural trade, for instance, government intervention policy on price, the agricultural futures market, international trade and other trade measurements related to agricultural products, and other interesting contemporary issues. Field : 9 Agricultural Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE493 | Applied Agricultural Economics Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Prerequisite(s): EE325 or EE425 and EE320 or EE421 Course Description: Study the application of theories and concepts in agricultural economics, using quantitative or qualitative analytical methods, on agricultural economic issues or related case studies, such as production and cost of production, consumer and market demand, agricultural product markets, production decisions, and investment possibilities, analyzing policy impacts on different aspects of agricultural product markets, agribusiness, food supply chain, food policy, and other interesting contemporary issues or case studies. Field : 9 Agricultural Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE499 | Seminar in Agricultural Economics Category: Capstone Project Prerequisite(s): Having completed at least two 400-level (or the above level) courses in the field of agricultural economics. Course Description: Seminar and research on topics in agricultural economics under the supervision of the lecturer. Field : 9 Agricultural Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE591 | Selected Topics in Agricultural Economics 1 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Studying topics in Agricultural Economics to be determined later. Field : 9 Agricultural Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
EE592 | Selected Topics in Agricultural Economics 2 Category: Elective Course for Major Area Study (400-level or above) Course Description: Studying topics in Agricultural Economics to be determined later. Field : 9 Agricultural Economics | 3 (3-0-6) |
Minor Area Study Courses
AC201 | Fundamental Accounting Category: Required Course for Finance minor Course Description: Basic principles, concepts, and procedures for collecting and recording accounting information; preparation and analysis of financial reports; accounting cycle; accounting and disclosure for assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity. Business | 3 (3-0-6) |
BA291 | Business in a Changing World Category: Required Course for both Finance or Marketing minor Course Description: Study the role of business in creating business value for sustainable success. Analyze stakeholder relationships, business environment, the collaborative elements of business including accounting, finance, marketing, production and operation, human resources, strategic management, entrepreneurship, and business ethics, in the changing world. Basic business concepts in different fields are integrated together through the implementation of business project. Business | 3 (3-0-6) |
ER211 | Introduction to Entrepreneurship Category: Elective Course for Minor Area Study Course Description: Concepts of entrepreneurship, theoretical applications of entrepreneurship, a start-up business or a new business development venture, analysis and evaluation of business opportunities, feasibility study, business planning design and business plan development. Business | 3 (3-0-6) |
HR201 | Modern Management and Entrepreneurship Category: Elective Course for Minor Area Study Course Description: Management concepts, evolution of management, roles and skills of managers, organizational functions and operations, planning, organizing, human resource management, leading, motivating, organizational behavior and performance, controlling, managerial decision making, ethics, and use of various management tools in the digital era. Also, modern entrepreneurship, current state of entrepreneurship in the global and Thailand contexts, concept and skills required for entrepreneurs, types and characteristics of entrepreneurs. Business | 3 (3-0-6) |
IS201 | Digital Technology for Business Category: Elective Course for Minor Area Study Course Description: Global business change, new business re-designed, IS and IT enhance business process, roles & types of information systems, business information systems, digital technology infrastructure, components of information technology infrastructure, trends of IT platform, database, data warehouse, big data, business intelligence, ethics, security, logical thinking, Microsoft Excel, Robotic process automation. Business | 3 (3-0-6) |
OM201 | Operations Management Category: Elective Course for Minor Area Study Course Description: Study of concepts, techniques and tools to design, analyze, and improve core operational capabilities, and their application to a broad range of industries. Topics include operations strategy, productivity, product/service design, process design, quality management, inventory management, project management, supply chain management, operational performance measurement and operations for sustainability. Business | 3 (3-0-6) |
FN201 | Business Finance Category: Required Course for Finance Minor Prerequisite(s): AC201 Course Description: The basic principles of financial management for business, the responsibilities of financial managers, maximization of enterprise value, axioms of finance, analysis of financial reports, cash flows, fundamental analysis on risk and rates of returns, the time value of money, working capital policies, capital budgeting techniques, financing mix, short-term and long-term sources of funds, distributions to shareholders, the costs of capital, and an introduction to developments in the financial industry, such as sustainable finance, digital assets Finance | 3 (3-0-6) |
FN211 | Financial Mathematics and Statistics Category: Required Course for Finance Minor Course Description: This class covers a broad range of topics that are critical foundations to the study of finance. The first part of the class covers exponential, logarithmic, linear, and quadratic functions as well as basic calculus. Calculus concepts include the principles of limits, differentiation rules, implicit differentiation, definite and indefinite integrals. Extended applications of these concepts are provided via modules on matrix algebra and optimization. The second part of the class focuses on probability and statistics. The aim is to develop familiarity with tools that are necessary building blocks in understanding algorithms behind machine learning and data analytics. The concept of prediction is introduced through basic econometrics of linear regression modeling and applied to financial forecasting problems. Finance | 3 (3-0-6) |
FN311 | Financial Management Category: Required Course for Finance Minor Prerequisite(s): FN201 and FN211 Course Description: Theoretical concepts of corporate financial management and their applications to resolving real-world financial problems that financial managers regularly encounter, management of asset structure and financial mix, applications of financial models and instruments on managing assets, liabilities, and equity, valuation, the cost of capital, capital structure, capital budgeting under uncertainty, leasing, concepts of agency problems and corporate governance. Sustainable finance and its effects on firm valuation. Finance | 3 (3-0-6) |
FN312 | Investments Category: Required Course for Finance Minor Prerequisite(s): FN201 and FN211 Course Description: Asset classes and financial instruments, securities markets and trading mechanism, risk and return measurement of individual securities and portfolios, efficient diversification, asset pricing models, efficient market hypothesis, bond pricing, yield curve, risks of bond investing, equity valuation: discounted cash flow and relative valuation, foundation of derivatives, valuation of futures and options Finance | 3 (3-0-6) |
FN313 | International Finance Category: Elective Course for Finance Minor Prerequisite(s): FN311, and EE212 or EC214 Course Description: Financial management of international and multinational businesses, international economic environment, international monetary system, current account, capital and financial account, balance of payment, the mechanism of foreign exchange market including cryptocurrencies and digital assets, application of financial instruments and derivatives for foreign exchange risk management, roles of international financial institutions, International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, Bank for International Settlement (BIS) Finance | 3 (3-0-6) |
FN424 | Investment Banking Category: Elective Course for Finance Minor Prerequisite(s): FN311 and FN312 Course Description: Principles of investment banking. Value creations for firms and investors by mergers and acquisitions and business reorganizations. Digital transformation of financial institutions. Variety of investment banking activities; restructuring, underwriting services, financial consulting services, initial public offerings, investment research, asset management and capital raising; through case studies in Thailand and abroad. Finance | 3 (3-0-6) |
FN456 | Derivatives Analysis Category: Elective Course for Finance Minor Prerequisite(s): FN312 Course Description: Fundamental principles of derivatives, including futures and forward contracts, options, warrants, swaps, and option embedded securities, derivatives pricing models, strategies for speculating or hedging. Finance | 3 (3-0-6) |
MK201 | Principles of Marketing Category: Required Course for Marketing minor Course Description: The central theme of this course is the introduction of the marketing definition and its importance as a vital business function. The content includes modern marketing concepts, the shift in marketing in the digital era, its role, and the major influences of marketing on the economy, society, environment, and consumer behavior. The course also covers the traditional marketing mix and the digital one, introductory marketing management, preparation of a basic marketing plan, and ethics of marketers. Marketing | 3 (3-0-6) |
MK211 | Consumer Behavior Category: Required Course for Marketing minor Prerequisite(s): MK201 Course Description: The central theme of this course is a study of concepts and theories of behavioral analysis to understand consumers and their behaviors. The content includes traditional thinking, which emphasizes psychological and behavioral theory for the purchasing decision-making process, and contemporary alternative theories from sociology and anthropology, which emphasizes understanding consumers from social and cultural dimensions. The course also covers different perspectives on ethical issues, including unethical business conduct and the dark side of consumer behavior. The content also focuses on the practical applications of consumer behavior analysis in marketing. Marketing | 3 (3-0-6) |
MK312 | Strategic Brand Management Category: Required Course for Marketing minor Prerequisite(s): MK211 Course Description: The central theme of this course is to introduce students to the overall responsibilities and tasks of a brand manager. The content includes developing and understanding different customer segments, the methodology to select the strategic target market(s), the design of brand positioning and identity, brand strategy and marketing programs, growing and sustaining brand equity, brand audit, and brand health check. Marketing | 3 (3-0-6) |
MK314 | Product and Service Management Category: Elective Course for Marketing Minor Prerequisite(s): MK211 Course Description: A central theme of the course is the study of management and planning of customer-centric product and service strategy. The content includes the definition, importance, and unique differences between products and services, as well as internal and external factors affecting management, market positioning, product and service decision strategies, such as customer experience-enhanced service marketing mix (7P’s), product mix, product line, product portfolio, and product and service life cycle management. The course also covers new product and service design and essential tools to create a positive customer experience and long-term organizational value, which are the Business Model Canvas, Service Blueprint, Innovative Product Development, and tools for monitoring, evaluating, and improving service quality, such as SERVQUAL and E-SERVQUAL models. Marketing | 3 (3-0-6) |
MK316 | Distribution Channel Management Category: Elective Course for Marketing Minor Prerequisite(s): MK201 Course Description: A central theme of the course is distribution channel systems for traditional and modern trade, their roles, management constraints, and integration into the marketing strategy. The content includes analysis of dynamic market factors, design and distribution of channels for effective and efficient management distribution networks, and strategic deployment of multi-channel marketing and omnichannel decisions to gain competitive advantages. The course also covers the roles, behavior of channel members, dimensions of channel power, management of channel conflict, channel incentive programs, coordination of channel relationships, and trade marketing, developing, controlling, and evaluating a distribution channel in consumer and business markets. Marketing | 3 (3-0-6) |
MK317 | Integrated Marketing Communications Category: Elective Course for Marketing Minor Prerequisite(s): MK312 Course Description: The central theme of this course is concepts, principles, and approaches to integrated marketing communications in response to the marketing challenge. The content includes an integrated marketing communications plan in terms of message and seamless contact point (digital and physical) integration and evaluation, based on the understanding of consumer and brand, especially brand positioning. Marketing | 3 (3-0-6) |
MK319 | Digital Marketing Strategy Category: Elective Course for Marketing Minor Prerequisite(s): MK312 Course Description: The central theme of this course is to educate students to understand how to apply digital technologies to craft marketing strategies in responding to consumer and business markets in a digital era. The content includes issues and challenges of digital technologies in the competitive marketing landscape, leveraging digital technologies to gain competitive advantage, formulating digital marketing strategy, and designing metrics to measure the success of digital marketing strategy. Marketing | 3 (3-0-6) |
MK322 | Retail Management Category: Elective Course for Marketing Minor Prerequisite(s): MK211 Course Description: The central theme of this course is a study of retail business management, based on shopper behavior understanding in order to determine effective retailing strategy and retail marketing mix so that the store can compete in the retail business, covering on-site, online, and Omni retail. The content includes retail concept development, location selection, store design and decoration, and category management, including determining the breadth and depth of product categories, purchasing, store layout, product display, retail pricing, promotion, and retail human resources. Marketing | 3 (3-0-6) |
MK326 | International Marketing Category: Elective Course for Marketing Minor Prerequisite(s): MK201 Course Description: The central theme of this course is a study of concepts and ways of doing international marketing, including importing and exporting, foreign direct investment, marketing strategy in globalization, and factors affecting international marketing through in-class assignments, case studies, and group projects. The content includes gaining consumer insights across international markets and translating them into appropriate marketing programs, linkages of the dynamic international environments, international opportunities, and international marketing strategies through an international marketing manager. Marketing | 3 (3-0-6) |
MK395 | Special Topics in Marketing 1 Category: Elective Course for Marketing Minor Prerequisite(s): MK312 Course Description: Philosophy, concepts, principles, tools, innovations, recent trends, and recent developments in marketing to develop students’ thinking and paradigmatic view that will be beneficial to their future careers. Marketing | 3 (3-0-6) |
3 (3 – 0 – 6) is referred to a course with 3 credits, 3-hour lecture, 0-hour laboratory session, and 6-hour self-study.
Course Plan
Year | Semester 1 | Credits | Semester 2 | Credits | Semester 3 | Credits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Year 1 | Gen-ed 1 – TU101 | 3 | Gen-ed 4 -TU103 | 3 | ||
Gen-ed 2 – TUxxx | 3 | Gen-ed 5 – TU106 | 3 | |||
Gen-ed 3 – TU100 | 3 | EE211 or EE212 | 3 | |||
EE211 or EE212 | 3 | MA216 or ST216 | 3 | |||
MA216 or ST216 | 3 | EL341 | 3 | |||
EL241 | 3
| AC201 (1) | 3 | |||
Year 2 | Gen-ed 6 – EL295 | 3 | Gen-ed 8 -TU116 | 3 | ||
Gen-ed 7 – TU122 | 3 | EE311 or EE312 | 4 | |||
EE311 or EE312 | 4 | EE325 or EE325 | 3 | |||
EE320 or EE325 | 3 | EE3xx or EE4xx –(6) | 3 | |||
BA291 — (2) | 3 | FN 201 or FN 211 — (4) | 3 | |||
FN 201 or FN 211 — (3) | 3 | MK201 or IS201 or OM201 or HR201 or ER201 or EExxx or Minor Area Study Courses- Free elective (1) | 3 | |||
Year 3 | Gen-ed 9 – EL 115 | 3 | Gen-ed 10 – xxx | 3 | EE300 or EE362 or EE365 | |
EE4xx — (1) | 3 | EE4xx — ( 4) | 3 | (Optional) | ||
EE4xx — (2) | 3 | EE4xx — (5)
| 3
| |||
EE3xx or EE4xx — (3) | 3 | EE404 or EE406 or EE460 | 3 | |||
FN311 or FN312 —- (5) | 3 | FN311 or FN312 —- (6) | 3 | |||
MK201 or IS201 or OM201 or HR201 or ER201 or EExxx or Minor Area Study Courses- Free elective (2 | 3 | FNxxx —– (7)
| 3 | |||
Year 4 | EE4xx — (7) | 3 | EE490 or EE470 or EE4x9 or EE500 | 3 | ||
EE4xx — (8) | 3 | EE3xx or EE4xx (10) | 3 | |||
EE4xx — (9) | 3 | |||||
EE215 (research methodology) | 3 | |||||
Minor — (8) | 3 | |||||
70 | 61 | 0 |
Year | Semester 1 | Credits | Semester 2 | Credits | Semester 3 | Credits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Year 1 | Gen-ed 1 – TU101 | 3 | Gen-ed 4 -TU103 | 3 | ||
Gen-ed 2 – TUxxx | 3 | Gen-ed 5 – TU106 | 3 | |||
Gen-ed 3 – TU100 | 3 | EE211 or EE212 | 3 | |||
EE211 or EE212 | 3 | MA216 or ST216 | 3 | |||
MA216 or ST216 | 3 | EL341 | 3 | |||
EL241 | 3
| Minor —– (1) | 3 | |||
Year 2 | Gen-ed 6 – EL295 | 3 | Gen-ed 8 – TU122
| 3 | ||
Gen-ed 7 – TU122 | 3 | EE311 or EE312 | 4 | |||
EE311 or EE312 | 4 | EE320 or EE325 | 3 | |||
EE320 or EE325 | 3 | EE3xx or EE4xx –(6) | 3 | |||
Minor — (2) | 3 | Minor — (3) | 3 | |||
IS201 or OM201 or HR201 or ER201 or EExxx or Minor Area Study Courses- Free elective (1) | 3 | IS201 or OM201 or HR201 or ER201 or EExxx or Minor Area Study Courses- Free elective (2) | 3 | |||
Year 3 | Gen-ed 9 – EL 115 | 3 | Gen-ed 10 – xxx | 3 | EE300 or EE362 or EE365 | |
EE4xx — (1) | 3 | EE4xx — ( 4) | 3 | (Optional) | ||
EE4xx — (2) | 3 | EE4xx — (5)
| 3
| |||
EE3xx or EE4xx — (3) | 3 | EE215 (research methodology)** | 3 | |||
Minor —- (4) | 3 | Minor —- (6) | 3 | |||
Minor —- (5) | 3 | FNxxx —– (7)
| 3 | |||
Year 4 | EE404 or EE406 or EE460 | 3 | EE490 or EE470 or EE4x9 or EE500 | 3 | ||
EE4xx — (7) | 3 | EE3xx or EE4xx (10) | 3 | |||
EE4xx — (8) | 3 | |||||
EE4xx — (9) | 3 | |||||
Minor — (8) | 3 | |||||
70 | 61 | 0 |
Year | Semester 1 | Credits | Semester 2 | Credits | Semester 3 | Credits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Year 1 | Gen-ed 1 – TU101 | 3 | Gen-ed 4 -TU103 | 3 | ||
Gen-ed 2 – TUxxx | 3 | Gen-ed 5 – TU106 | 3 | |||
Gen-ed 3 – TU100 | 3 | EE211 or EE212 | 3 | |||
EE211 or EE212 | 3 | MA216 or ST216 | 3 | |||
MA216 or ST216 | 3 | EL341 | 3 | |||
EL241 | 3
| Minor —– (1) | 3 | |||
Year 2 | Gen-ed 6 – EL295 | 3 | Gen-ed 8 -TU116 | 3 | ||
Gen-ed 7 – TU122 | 3 | EE311 or EE312 | 4 | |||
EE311 or EE312 | 4 | EE320 or EE325 | 3 | |||
EE320 or EE325 | 3 | EE3xx or EE4xx –(6) | 3 | |||
Minor — (2) | 3 | Minor — (3) | 3 | |||
EExxx or Minor Area Study Courses- Free elective (1)
| 3 | EExxx or Minor Area Study Courses- Free elective (2)
| 3 | |||
Year 3 | Gen-ed 9 – EL 115 | 3 | Gen-ed 10 – xxx | 3 | EE300 or EE362 or EE365 | |
EE4xx — (1) | 3 | EE4xx — ( 4) | 3 | (Optional) | ||
EE4xx — (2) | 3 | EE4xx — (5)
| 3
| |||
EE3xx or EE4xx — (3) | 3 | EE215 (research methodology)** | 3 | |||
Minor —- (4) | 3 | Minor —- (6) | 3 | |||
Minor —- (5) | 3 | FNxxx —– (7)
| 3 | |||
Year 4 | EE404 or EE406 or EE460 | 3 | EE490 or EE470 or EE4x9 or EE500 | 3 | ||
EE4xx — (7) | 3 | EE3xx or EE4xx (10) | 3 | |||
EE4xx — (8) | 3 | |||||
EE4xx — (9) | 3 | |||||
Minor — (8) | 3 | |||||
70 | 61 | 0 |